1. The Essence of Agile: Principles and Values
a. Customer Collaboration over Contract Negotiation
Agile places a premium on customer collaboration, emphasizing the importance of working closely with stakeholders to understand and meet their evolving needs. This dynamic engagement ensures that the end product aligns with user expectations.
b. Responding to Change over Following a Plan
In Agile, adaptability takes precedence over rigid plans. The methodology embraces change, understanding that requirements may evolve throughout the development process. This flexibility allows teams to respond effectively to emerging challenges and opportunities.
2. Agile Frameworks: Scrum, Kanban, and More
a. Scrum: Iterative and Incremental
Scrum, a popular Agile framework, structures development into time-boxed iterations called sprints. This iterative approach enables teams to deliver functional increments of the product at the end of each sprint, fostering continuous improvement.
b. Kanban: Visualizing Workflow
Kanban emphasizes visualizing the workflow, making work items visible on a Kanban board. This framework promotes a steady flow of work, minimizing bottlenecks and enhancing the team’s ability to adapt to changing priorities.
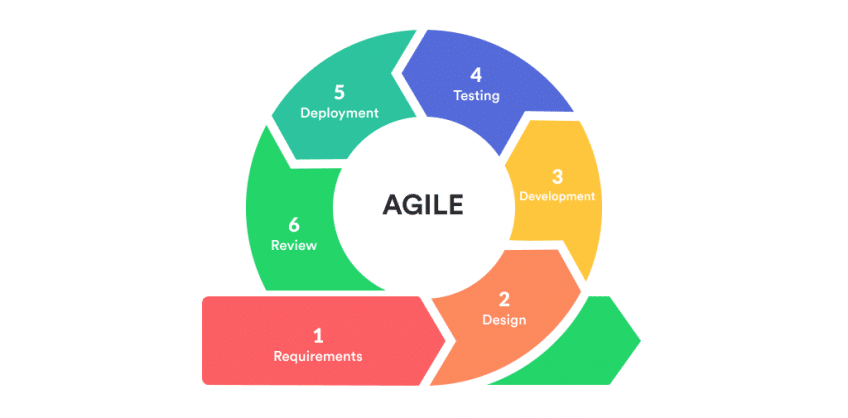
3. Iterative Development and Continuous Feedback
a. Sprints and Iterations
www.softwarechiefs.com/ embraces the concept of iterations, dividing the development process into smaller, manageable cycles. This iterative approach allows teams to deliver functional increments regularly, ensuring a steady rhythm of progress.
b. Continuous Feedback Loops
Regular feedback loops, both within the team and with stakeholders, are integral to Agile. Continuous feedback facilitates early detection of issues, enables quick course corrections, and ensures the final product aligns with user expectations.
4. Cross-Functional Collaboration and Empowered Teams
a. Cross-Functional Teams
Agile promotes the formation of cross-functional teams comprising members with diverse skill sets. This collaborative structure enhances communication, accelerates decision-making, and ensures a holistic approach to problem-solving.
b. Empowered Teams
Agile empowers teams to self-organize and make decisions collectively. This autonomy fosters a sense of ownership, accountability, and motivation among team members, driving them to deliver high-quality results.
5. Agile Artifacts: User Stories, Backlogs, and Burndown Charts
a. User Stories
User stories serve as concise descriptions of functionality from an end user’s perspective. They help prioritize development efforts based on user value, ensuring that features align with customer needs.
b. Backlogs and Burndown Charts
Product backlogs outline the features, enhancements, and fixes planned for a product. Burndown charts visually track the team’s progress, providing a snapshot of completed work versus the remaining workload during a sprint.
6. Agile in Practice: Realizing Benefits and Challenges
a. Benefits of Agile
- Faster Time-to-Market: Agile’s iterative approach accelerates the delivery of functional increments.
- Enhanced Flexibility: The methodology adapts to changing requirements and priorities.
- Improved Quality: Continuous feedback loops enable early detection and resolution of issues.
b. Challenges of Agile
- Adaptation Challenges: Teams new to Agile may face initial struggles adapting to its principles.
- Stakeholder Collaboration: Effective customer collaboration requires proactive engagement and communication.
- Overemphasis on Speed: Prioritizing speed over other factors may compromise quality.
Conclusion: Agile’s Evolutionary Journey in Software Development
Agile software development stands as a testament to the industry’s commitment to adaptive excellence. By prioritizing collaboration, flexibility, and continuous improvement, Agile has reshaped how teams approach projects, fostering a culture of responsiveness and innovation.
Embrace the Agile mindset, navigate the dynamics of change, and embark on a journey where software development is not just a process but a collaborative, iterative, and customer-centric endeavor.